Source: https://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/21f/21f.027/opium_wars_01/ow1_essay01.html
(Hover over India and China on this map)
The adverse effects of The Opium Trade on China
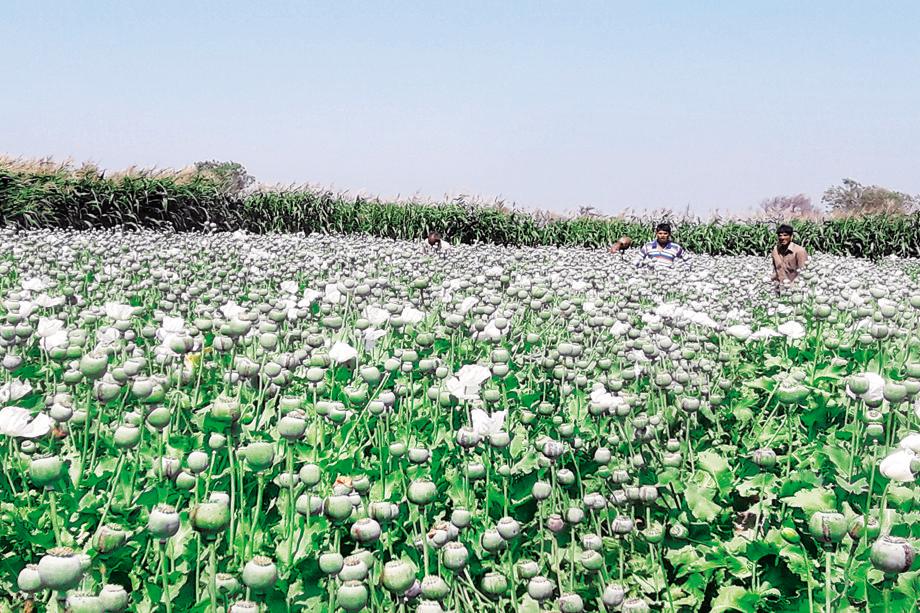
Opium was cheap in China and the lower class, the labor class, of society was the ones most affected by Opium. Due to that, productivity decreased on a large scale as the labor would be smoking Opium instead of working. Due to that, work slowed down and got so bad, that the Emperor got involved by banning the import of Opium starting in 1724 (But it was ineffective as British merchants used Chinese merchants to smuggle it in).The Treaty of Nanking
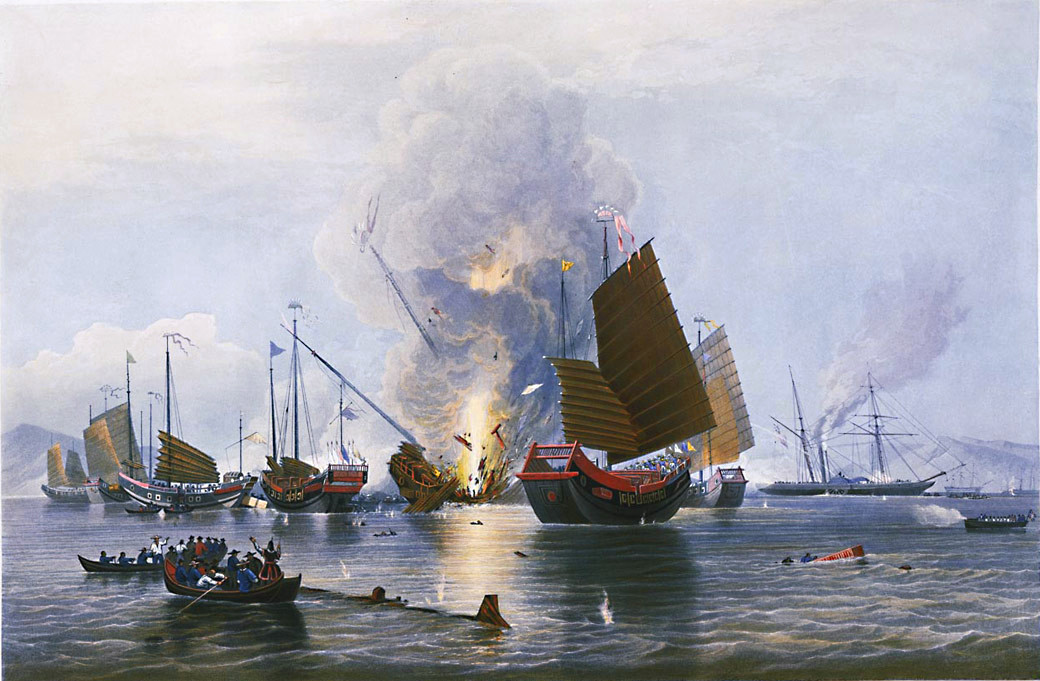
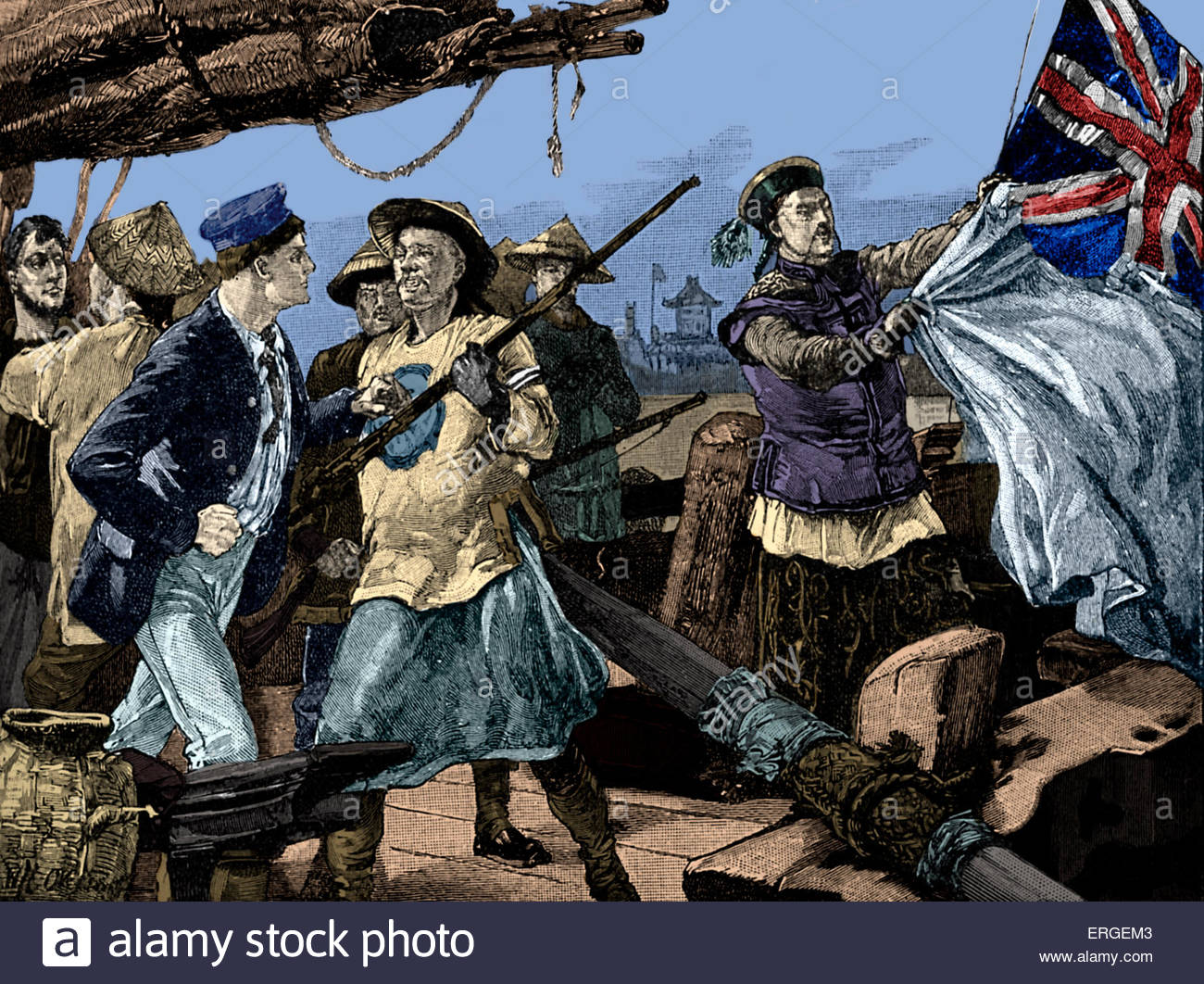
The first Opium war, aggravated due to cultural differences (China felt superior) & diplomatic differences, was won by Britain. The treaty of Nanjing was signed and the conditions were:- 4 Additional ports opened for trade with the west (China had only allowed a few ports prior to this condition as they had a closed door trading system)
- Britain had extraterritorality - They were subject to their own laws in China
- The British residing in China were subject to special rights in their living areas
- 21 million silver dollars (Currency) was to be paid to Britain to compensate for the war, along with additional compensations for the Opium the Chinese had salvaged and destroyed
- China had to treat Britain as an equal for all future trades rather than an inferior
- Britain gets Hong Kong (Port City)
- Britain gets most favoured nation status (Gets any rights that China grants to other countries during trade)
The Treaty of Tientsin
After the second Opium war, the treaty of Tientsin was signed. The conditions were much worse, as compared to the conditions of the treaty of Nanking. The conditions are as follows:- 6 more ports were to be made open for trade with Britain
- OPIUM WAS FULLY LEGALIZED TO BE IMPORTED INTO CHINA, WITH SMALL IMPORT FEES
- Christian Missionaries were given complete freedom to convert people to Christianity
- Europeans allowed to travel freely in China (Travel restriction lifted)
- Ambassadors of European Countries could open homes in Beijing - The imperial capital of China (This is a big thing as only people of high class in the Chinese society could reside here and letting any ambassador live in the city is a big insult to China


